How does empirical process control apply to Agile Scrum?
Posted bySCRUMstudy® on August 14, 2024
Categories Agile Iterative Development Product Development Scrum Scrum Principles
Agile Scrum emphasizes empirical process control, a key principle that underpins its effectiveness in project management. Unlike traditional approaches that rely heavily on predictive planning and fixed processes, empirical process control in Scrum embraces adaptability and learning through experience.
In today’s rapidly changing market trends, the customer may imagine an ‘apple’ and the finished product made by the project team may be an ‘orange’. This though is not the main problem. If the customer is aware of what’s cooking from the start he can steer the team to the ‘apple’ side. But in actuality the customer finds out about the ‘orange’ only too late. In other words if inputs and processes are in control and are reliable, we can get reliable outputs (which are generally the case with Waterfall model). The problem arises when inputs and processes cannot be controlled rigidly which generally means that the outputs would be unreliable (the Agile/Scrum scenario). In such circumstances we need to look beyond the waterfall model and focus on Empirical Process Control which simply means you need to look at the outputs more frequently and if it is not as per your liking you go back to inputs and processes and tweak it accordingly.
In Scrum, decisions are made based on observation and experimentation rather than on detailed upfront planning. Empirical process control relies on the three main ideas of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
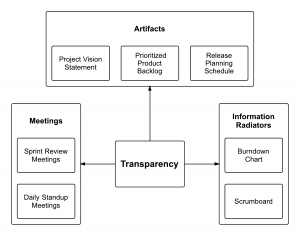
Transparency allows all facets of any Scrum process to be observed by anyone. This promotes an easy and transparent flow of information throughout the organization and creates an open work culture. In Scrum we have a Project Vision Statement which can be viewed by all stakeholders and the Scrum Team; an open Product Backlog with prioritized User Stories, both within and outside the Scrum Team; clearly visible Scrumboards, Burndown Charts, and other information radiators; Daily Standup Meetings conducted making sure everyone’s aware of everything; and Sprint Review Meetings in which the Scrum Team demonstrates the potentially shippable Deliverables.
The following figure summarizes the concept of transparency in Scrum
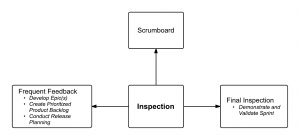
Inspection in Scrum is depicted through the use of a common Scrumboard; collection of feedback from the customer and other stakeholders; review and approval of the Deliverables by the Product Owner and the customer.
The following figure summarizes the concept of inspection in Scrum:
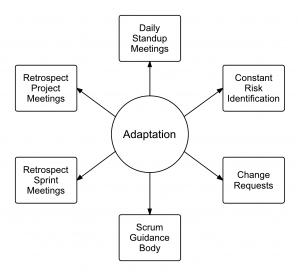
Adaptation happens as the Scrum Core Team and Stakeholders learn through transparency and inspection and then adapt by making improvements in the work they are doing. In Daily Standup Meetings, Scrum Team members openly discuss impediments to completing their tasks and seek help from other team members. Risk identification is performed and iterated throughout the project. Improvements can also result in Change Requests, which are discussed and approved. The Scrum Guidance Body interacts with Scrum Team members during many processes to offer guidance and also provide expertise as required. During the Sprint Retrospective, agreed actionable improvements are determined.
The following figure summarizes the concept of adaptation in Scrum:
These three pillars of Empirical Process Control ensure that the problems which projects face in the Traditional Waterfall way of doing things do not happen in Scrum Projects.